|
|

|
The reactor model selected by KEDO as the reference plant design for the LWR project is the ROK's Korean Standard Nuclear Power Plant (KSNP, see image below). The design is a result of cooperative efforts between the Korea Power Engineering Company (KOPEC), which is the architect engineer and nuclear steam supply system (NSSS) designer, DOOSAN Heavy Industries & Construction Company (for fabrication and procurement of the NSSS), the KEPCO Nuclear Fuel Company (for nuclear fuel), and various construction and startup contractors.
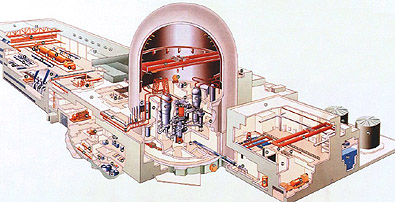
There are a total of twelve KSNP plants either in operation or in stages of construction in the Republic of Korea (ROK): seven plants are in operation, one is in commissioning, and four are under construction.
|
Unit
|
Status
|
|
Ulchin Units 3 and 4
|
Operating (1998 & 1999)
|
|
Yonggwang Units 5 and 6
|
Operating (2001 & 2002)
|
|
Ulchin Unit 5
|
Operating (2004)
|
|
Ulchin Unit 6
|
In commissioning
|
|
Shin Wolsung Unit 1 and 2
|
Under construction
|
|
Shin Kori Unit 1 and 2
|
Under construction
|
Ulchin Units 3 and 4 are the lead units of the KNSP and are the reference plant for the LWR project. Design and operational improvements have been made to the KSNP units following the Ulchin 3 and 4 units as a result of experience and lessons learned during design, construction and operations of these initial units. These improvements are included on the LWR project.
The KSNP NSSS is a two-loop design and is a scaled down and updated version of the Combustion Engineering (CE) System 80 pressurized-water reactor design, which is based on the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission-approved CE Standardized Safety Analysis Report (CESSAR-F). There are three nuclear power units in operation in the United States with System 80 nuclear steam supply systems (i.e., Palo Verde Units 1, 2 and 3). However, the thermal power for the KSNP was reduced and additional design improvements provided to obtain additional thermal margin for safety. Thus, each unit is rated at 1000 MWe rather than the 1300 MWe of the original System 80 design.
Additionally, the KSNP was developed through the consistent application of fundamental design principles, which are comparable with Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) advanced light-water reactor (ALWR) programs, and include the concepts of enhanced safety, simplicity, increased design margin, the use of proven technology, and more effective design and construction processes. Regulatory stabilization is achieved by resolving open licensing issues, establishing acceptable severe accident provisions, and designing the plant consistent with regulatory criteria. Regulatory practice in the ROK refers to that in the United States for areas that are not specified in Korean regulations. There are three levels of safety: accident resistance, core damage prevention, and mitigation.
The LWR plant is based on designs that have been licensed in both the United States and the ROK, which would have an appreciable operating record before the LWR units begin operation. The KSNP's use of proven technology and the operating and construction experience of existing plants also offer a strong regulatory basis for the LWR plant.
|

|

|

|
|

|

